The joints of the human body withstand daily stress, so they become susceptible to various types of destructive factors. Among the diseases of the joints, arthrosis is often found, which affects both large and small joints. Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a degenerative-dystrophic damage of the knee joint, in which its motor activity is impaired. In the absence of appropriate treatment, the disease can lead to disability.
Because the disease provokes characteristic deformities in the joint, it is called deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, which correctly describes the typical characteristics of the pathology. The disease is chronic and is more commonly diagnosed in women who also suffer from overweight and venous pathology of the lower extremities, but there may be other causes. Due to age changes, it also occurs in older people.
Osteoarthritis in young people can be caused by injuries. As a result of degenerative-dystrophic changes, the cartilage softens, exfoliates and is covered with cracks of different depths. Subsequently, he ceased to perform his function.
The reasons
Various causes lead to the appearance of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint. Traumatic factor is a common cause. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis can develop as a result of a sprain or fracture in that area, as well as injury to the meniscus. Gonarthrosis of the knee joint usually occurs in young people who are active in sports, or in those people whose work is associated with increased mobility, lifting and carrying heavy loads.
Few people know that such an injury can be the result of treatment when the injury itself has already healed, but prolonged immobilization of the limb has caused circulatory disorders in this area. Due to this, gonarthrosis appeared.
Increased physical activity of the knee is one of the leading factors in the onset of the disease. It most often affects athletes who have constant active loads on the knee. At a young age, osteoarthritis may not appear, usually rapid changes begin after cessation of physical activity.
There is also a risk of disease in those people who do not reduce the strain on the joints, even in adulthood. In such athletes the risk of fractures and dislocations increases, microtraumas appear. Therefore, after forty years, doctors recommend athletes to reduce the load, to switch to coaching. Running and squats are best avoided, as these are the activities that put the most strain on the knee joint. One limb is most commonly affected and left gonarthrosis or right gonarthrosis occurs.
An important factor in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee is the removal of the menisci. If for some reason the menisci have been removed, then in 90 percent of cases this leads to osteoarthritis - the so-called knee loop occurs, in which the joints experience more friction than usual.
The problem of overweight is also relevant for people with osteoarthritis. Excess weight puts unnecessary pressure on the joints. As a result, it is not the cartilage itself that is damaged, but the meniscus. And in combination with overweight and varicose veins of the lower extremities threatens the emergence of acute osteoarthritis.
Weak ligaments in some patients are a congenital feature, and sometimes the ligaments are affected due to other diseases. In one way or another, weak ligaments provoke increased mobility in the joint, due to which the joint surfaces are significantly scraped. The effects of poor ligaments may not be felt for long until patients experience symptoms of true osteoarthritis.
Joint pathologies also lead to the development of the disease. The most common cause of osteoarthritis is arthritis - inflammation of the joints. In arthritis, there are typical signs - deterioration of the composition of synovial fluid, pathological changes in cartilage, swelling, redness of soft tissues. Even after osteoarthritis is cured, chronic processes lead to the appearance of osteoarthritis.
Disorders of metabolic processes often lead to pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Bones and joints lack the nutrients and minerals that are so essential for tissue strength. In their absence, bones and cartilage surfaces are subject to destructive processes, therefore, even with light exercise, primary osteoarthritis occurs.
Symptoms
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is manifested by a set of characteristics that are difficult to miss. The signs are not felt only in the first stage of the pathology, but already the second and third degree give clear symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint:
- pain- one of the key characters that does not appear immediately. Interestingly, with the development of osteoarthritis, the pain may not be felt for several months or years until the disease worsens. Usually the first signs of pain are discomfort when exercising, walking or running, but it also occurs when the meniscus is pinched. In the second degree of arthrosis the pain in the joint is felt more strongly, and in the third degree of development painful sensations appear even at rest. The attacks intensify even after short walks without putting much strain on the joint, so patients try to spare their knees;
- deformation- The manifestations become more pronounced in the third stage of the development of osteoarthritis. The knee will retain its normal shape, but will look slightly swollen and edematous. When arthritis joins, the knee will become red, hot and painful to the touch;
- crunchingwith osteoarthritis occurs in the second and third stages of the disease. Crispy sounds are different from the healthy clicks that can sometimes be heard when the knee is stretched and bent. In osteoarthritis, the symptoms are characterized by a dry, harsh sound that appears abruptly and is accompanied by pain;
- synovitis- accumulation of a certain amount of fluid in the joint cavity. It is there and it is normal. But the accumulation of excess leads to the development of a cyst - the most noticeable Baker's cyst, which can be identified in the unfolded position of the leg;
- limited mobility in the knee- a typical sign of pathology, as patients first try to consciously protect themselves from pain, and in the late stage of osteoarthritis can not straighten the limb at all. In the third stage of development, deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint (DOA) completely leads to loss of movement. Patients adapt to move on bent legs while using support devices.
Degrees of development
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint goes through three stages in its development.
In osteoarthritis of the 1st degree the pain is insignificant and occurs only during active physical activity on the knee joint. In the first degree, fluid can accumulate in the cavity, which in the second and third is already a cyst. As the pain progresses, it appears during movement, but passes quickly. Externally, the deformity of the knee joint is invisible, so diagnosing osteoarthritis of the knee joint can be difficult.

In second-degree disease, the damage to cartilage tissue is more significant. If you take an X-ray, then it already shows the stage of bone growth. With each movement there is a sharp sudden pain in the knee, but returning to a comfortable position, the knee no longer hurts. In the second stage of DOA, you may hear a crunch typical of osteoarthritis. As you progress, the problems with knee extension and flexion get worse. The deformation becomes noticeable externally.
Third degree osteoarthritis of the knee joint is characterized by significant thinning of cartilage tissue. Gradually, the cartilage wears out so much that the bone is exposed in some areas. The X-ray image shows a significant amount of osteophytes - bone growths, salts that have appeared in the joint cavity. Externally, the changes are clearly visible and the patient is worried about constant pain. It is not difficult to diagnose - a visual examination is sufficient and X-ray control is performed.
With the progression of this degree, osteoarthritis can lead to complete loss of functionality. Osteoarthritis of the knee joint may join at any stage of the pathology.
Treatment
Dealing with osteoarthritis of the knee is not easy, especially if the disease is advanced or has joined inflammation and arthritis has developed.
conservative
The group of the most active drugs against osteoarthritis are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These are mainly cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, they can perfectly relieve inflammation, swelling and contribute to rapid recovery.
These drugs have significant limitations, so they should not be used without a doctor's recommendation. For example, they are able to exacerbate stomach ulcers, heart disease, urinary tract pathology. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also prohibited during pregnancy.
The second group of agents are chondroprotectors, which improve the characteristics of cartilage tissue. They are used in osteoarthritis to restore the proper structure of cartilage, because in the process of resolving it loses many important components - chondroitin and glucosamine. Therefore, almost all chondroprotectors contain both substances, but some preparations are one-component.
With the help of these drugs it is possible to help the patient in the first and second stages of the disease, but not in the third, when irreversible changes have occurred.
During conservative therapy, the doctor will also give recommendations on nutrition. If the patient or patient is overweight, it is mandatory to follow a diet to normalize weight. How to strengthen a stable weight - the doctor will also tell. It is also not recommended to eat a lot of salt, but it is better to fill the diet with calcium, vitamins and minerals. Jelly, jelly will be useful.
Operational
The most common type of surgery for osteoarthritis is arthroscopy, but other interventions are performed. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee is usually performed in the second and third degree, when conservative therapy no longer helps.
If minimally invasive intervention is required, for example when fluid accumulates in the knee joint, it is possible to do it with a puncture. A puncture is made in the cavity of the knee joint and the excess fluid is pumped out. This method can both diagnose a disease and simultaneously apply it for treatment. The fluid is taken in the initial stage in a minimal amount, but this already significantly improves the well-being of patients. Then, after examining the biomaterial, another part is removed and corticosteroids are injected into the joint cavity.
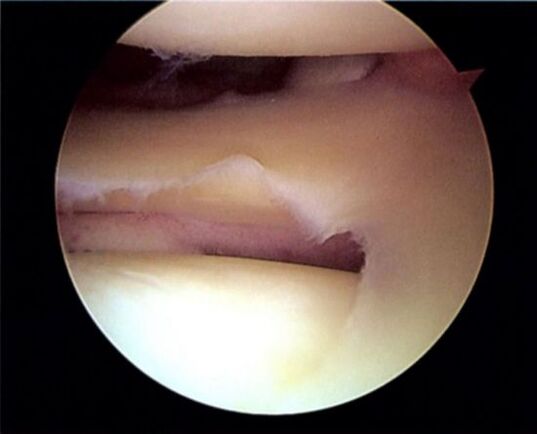
Arthroscopy is the most common. Through a small incision in the skin, several instruments are introduced, which make it possible to examine the joint and the necessary manipulations in it. With the help of arthroscopy, it is possible to remove tissue particles that have separated from the cartilage, but there is always a risk of secondary gonarthrosis.
In severe injuries, periarticular osteotomy is required. This is a larger impact on the joint, as a result of which it is sawn a little and adjusted to the desired angle. After the operation, the rehabilitation is longer, but the effect lasts longer.
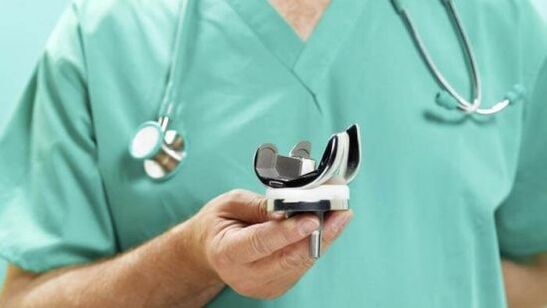
Significant destruction of the joint elements leads to complete immobilization of the limb. The joint does not perform its function, which means that it must be replaced and surgery performed. Knee arthroplasty is an expensive operation, but in itself allows the patient to return to movement in the limb. Different knee prostheses are installed - plastic, ceramic or metal. These are durable structures that allow you to forget about the problem for decades.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods can be used only when the acute period has passed and the patient recovers.
Actively used methods include:
- ozone therapy- exposure of the affected joint with ozone, the substance may be injected or used as an external treatment. This type of patient care is very effective and is therefore often used in the treatment of various pathologies, including osteoarthritis. The treatment allows to activate the blood circulation in the problem area, to achieve anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. At the same time, treatment with glucocorticoids is carried out;
- kinesiotherapy- The treatment is performed with the help of a special set of exercises. The load is formed taking into account individual data, and when performing exercises using special simulators that strengthen the joints. The difference between kinesiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises is the active effect not only on the arthrosis of the knee, but also on the whole body as a whole.
Apply not only ozone therapy and kinesiotherapy, but also physiotherapy. The author's methods of exercises to eliminate osteoarthritis of the knee give good results. During and after the exercises it may be necessary to wear a special knee brace - an orthosis, to strengthen the right or left knee joint.


















